See Snapshots archive.
Snapshot for March 5, 2008.
Teacher pay disadvantage soars
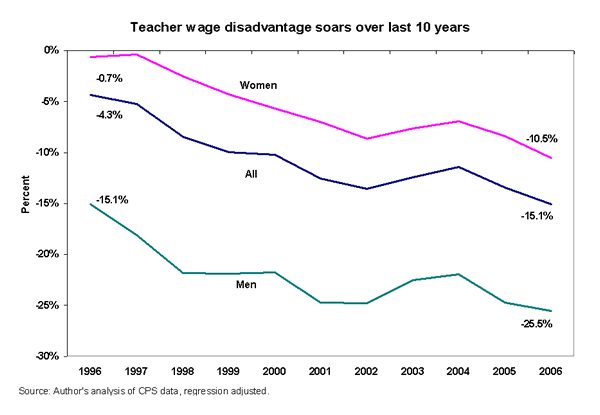
In 2006, public school teachers earned 15.1% lower weekly earnings than other employees with comparable education credentials and experience earned. In 1996, this wage disadvantage was only 4.3% (see Chart). Although the wage disadvantage for both male and female teachers has grown substantially over the last 10 years, in 2006 the gap was far larger among males (25.5%) than females (10.5%).
What happened? The earnings gains that benefited college-educated (and other) workers during the late 1990s appear to have bypassed teachers. Moreover, in recent years, real wages have stagnated for the average college graduate, and teachers appeared to have fared even worse.
This erosion of teacher pay relative to those of other opportunities affects the trends in teacher quality that are so critical to improving education outcomes. If the goal is to improve the quality of the typical teacher, then raising teacher compensation is a critical component in any strategy to recruit and retain a higher-quality teacher workforce.
This week’s Snapshot previews data to be presented as part of the forthcoming EPI book, The Teaching Penalty: Teacher Pay Losing Ground by Sylvia Allegretto, Sean Corcoran, and Lawrence Mishel. The book will be available at www.epi.org on March 7, 2008.