Cumulative change in total economy productivity and real hourly compensation of production/nonsupervisory workers, 1948–2013
| Year | Real hourly compensation | Productivity |
|---|---|---|
| 1948 | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 1949 | 6.3% | 1.5% |
| 1950 | 10.5% | 9.3% |
| 1951 | 11.8% | 12.4% |
| 1952 | 15.0% | 15.6% |
| 1953 | 20.8% | 19.5% |
| 1954 | 23.5% | 21.6% |
| 1955 | 28.7% | 26.5% |
| 1956 | 33.9% | 26.7% |
| 1957 | 37.1% | 30.1% |
| 1958 | 38.2% | 32.8% |
| 1959 | 42.6% | 37.6% |
| 1960 | 45.5% | 40.0% |
| 1961 | 48.0% | 44.4% |
| 1962 | 52.5% | 49.8% |
| 1963 | 55.0% | 55.0% |
| 1964 | 58.5% | 60.0% |
| 1965 | 62.5% | 64.9% |
| 1966 | 64.9% | 70.0% |
| 1967 | 66.9% | 72.1% |
| 1968 | 70.7% | 77.2% |
| 1969 | 74.7% | 77.9% |
| 1970 | 76.6% | 80.4% |
| 1971 | 82.0% | 87.1% |
| 1972 | 91.3% | 92.0% |
| 1973 | 91.3% | 96.7% |
| 1974 | 87.0% | 93.6% |
| 1975 | 86.9% | 97.9% |
| 1976 | 89.7% | 103.4% |
| 1977 | 93.2% | 105.8% |
| 1978 | 96.0% | 107.8% |
| 1979 | 93.4% | 108.1% |
| 1980 | 88.6% | 106.5% |
| 1981 | 87.6% | 111.0% |
| 1982 | 87.8% | 107.9% |
| 1983 | 88.3% | 114.1% |
| 1984 | 87.0% | 119.7% |
| 1985 | 86.4% | 123.4% |
| 1986 | 87.3% | 128.0% |
| 1987 | 84.6% | 129.1% |
| 1988 | 83.9% | 131.8% |
| 1989 | 83.7% | 133.7% |
| 1990 | 82.2% | 137.0% |
| 1991 | 81.9% | 138.9% |
| 1992 | 83.1% | 147.6% |
| 1993 | 83.4% | 148.4% |
| 1994 | 83.8% | 150.8% |
| 1995 | 82.7% | 150.9% |
| 1996 | 82.8% | 157.0% |
| 1997 | 84.8% | 160.6% |
| 1998 | 89.2% | 165.9% |
| 1999 | 92.0% | 172.8% |
| 2000 | 93.0% | 179.2% |
| 2001 | 95.7% | 183.5% |
| 2002 | 99.6% | 191.4% |
| 2003 | 101.8% | 200.9% |
| 2004 | 101.1% | 209.1% |
| 2005 | 100.2% | 214.5% |
| 2006 | 100.3% | 216.5% |
| 2007 | 101.8% | 218.8% |
| 2008 | 101.9% | 219.4% |
| 2009 | 109.9% | 226.0% |
| 2010 | 111.8% | 235.4% |
| 2011 | 109.3% | 236.7% |
| 2012 | 107.5% | 240.9% |
| 2013 | 108.9% | 243.1% |
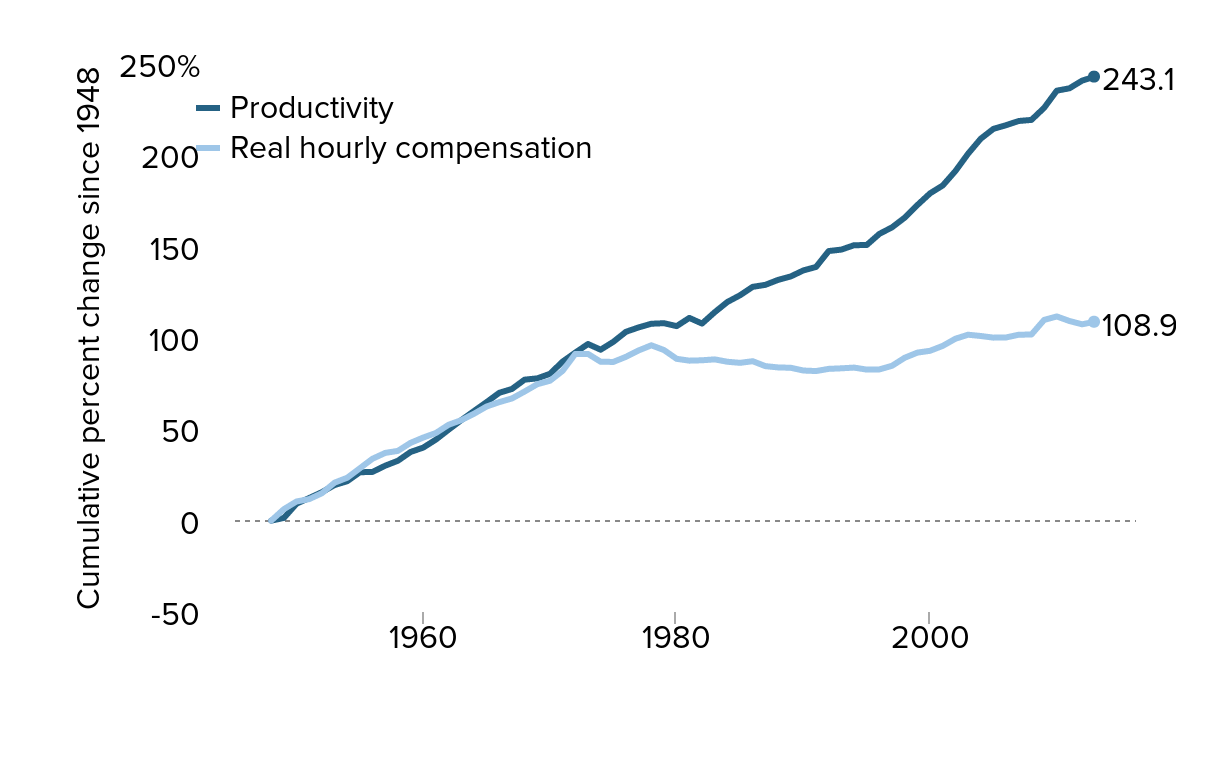
Note: Data are for compensation of production/nonsupervisory workers in the private sector and net productivity of the total economy. "Net productivity" is the growth of output of goods and services less depreciation per hour worked.
Productivity is based on unpublished Total Economy Productivity data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics Labor Productivity and Costs program. Hourly compensation for production/nonsupervisory workers is based on the wage data series used in SWA Table 4.3. Wages are converted to hourly compensation by scaling by the real compensation/wage ratio from the NIPA data used in SWA Table 4.2.
Source: EPI analysis of unpublished Total Economy Productivity data from Bureau of Labor Statistics Labor Productivity and Costs program and wage data from BLS Current Employment Statistics, BLS Employment Cost Trends, and Bureau of Economic Analysis National Income and Product Accounts
Previous chart: « Thinking beyond the minimum wage fight
Next chart: The share of the unemployed who have been jobless for six months or more, 1948–2014 »